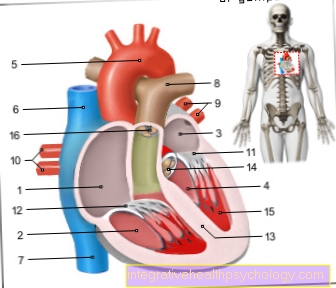
Knock knees
Synonyms in the broadest sense
Medical: Genu valgum
English: knock-knee, in knee, genu valgum
definition
X-legs are axis deviations from the normal axis. In contrast to bow-legged legs, the axis deviates inward on X-legged legs. When viewed from the front, the impression of an "X" is created.
Summary
Knee legs are axis deviations from the norm. The legs deviate in the middle to the side and give the impression of an "x". Knock knees can be both congenital and acquired.
In addition to pain, there is also the complaint Osteoarthritis of the knee in front. The Knee joint is worn on one side.
The diagnosis is primarily clinical, i.e. based on the symptoms and appearance as well as a targeted one Treadmill analysis posed. That too X-ray image is indicative, especially with the arthrosis of the joint.
Treatment of the underlying disease as well as surgical treatment are available for therapy.
causes
Knock knees can be both congenital and acquired.
Congenital knock knees:
In the case of congenital knock knees, weaknesses in the connective tissue are the main issues. A malformed bone can also be congenital.
Knock-knees in children with 2.5 years of age are "normal" and should grow straight again in the further course.
Acquired knock knees:
1. Acquired knock knees can be symptoms of various underlying diseases:
- Rickets (vitamin D deficiency)
- Brittle bones after the Menopause
- Hormonal imbalances
- Inflammation
- Obesity
- Tumors
2. Incorrect growth
3. After bone fractures (medically post-traumatic)
4. Also at Paralysis Knock knees can develop when the direction of growth is changed by an asymmetrical muscle pull.
Appointment with a knee specialist?
I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is dr. Nicolas Gumpert. I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
The knee joint is one of the joints with the greatest stress.
Therefore, the treatment of the knee joint (e.g. meniscus tear, cartilage damage, cruciate ligament damage, runner's knee, etc.) requires a lot of experience.
I treat a wide variety of knee diseases in a conservative way.
The aim of any treatment is treatment without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You can find me in:
- Lumedis - your orthopedic surgeon
Kaiserstrasse 14
60311 Frankfurt am Main
Directly to the online appointment arrangement
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
Further information about myself can be found at Dr. Nicolas Gumpert
Symptoms
Not just cosmetic Knock knees problematic in adults, especially increased exposure to the Knee joint is the consequence.
The asymmetrical load on the knee joint leads to increased wear of the external share of the joint. Not only does the articular cartilage wear out, causing premature wear, but also the external one meniscus (especially the outer meniscus) suffers. The result is knee osteoarthritis.
The knock knees often come together with one Buckle foot and a leg bent backwards (so called Genu recurvaturum) on.
diagnosis
The diagnosis is of course made clinically in pronounced forms. The misalignment can be easily recognized from the outside without any problems. An X-ray can be helpful for lighter forms. Here are the Thigh bone, the knee joint to the Ankle joint X-rayed in a so-called axis recording. In order to objectively record the extent of the deformation, an imaginary line is drawn from the Femoral neck of the thighbone pulled through the knee joint to the ankle. Normally this line goes right through the knee joint. With knock knees, this connecting line hits the knee joint too far outside.
Knock knees: what to do?

If the knock knees persist to too much, there is several options for action:
First, one surgical correction of the knee, more on that later.
Secondly, Insoles in the shoes, or on the inside of the shoe. This will make the The foot and lower leg are tilted outwards (quasi in If a-Direction) and the load on the knee changes: The pressure is removed from the outside of the knee and increased shifted to the inside of the knee - just as if the leaning tower of Pisa were being straightened by wedges in the foundation.
The third option is to be seen and nothing to do. While this up to the age of eight can still be useful, should with the onset of puberty with continued knock-knees position therapy definitely takes place. There are not only cosmetic but also orthopedic reasons for this: the knee becomes bow-legged or knocked-out unevenly loaded. As a result, the underlying cartilage- and Bone tissue wears out and degenerates much faster.
Knee damage, Pain and massive malpositions incorrect movements are the result. Over time this can be a Endoprosthesis - a artificial knee joint or artificial hip joint make necessary.
Furthermore, a misalignment of the legs also affects the entire body With Spine and move from what to other orthopedic problems leads - in view of the uncomplicated treatment a thoroughly avoidable evil.
Conclusion: Malposition up to the age of 8 quite normal can be (up to 20 degrees deviation), should if continued a correction or treatment take place. Come to clarify any leg deformity Pediatrician or orthopedist in question.
How are knock knees corrected?
There are several ways to correct knock knees.
Besides the conservative therapy With Shoe insoles on the inside of the shoe or physiotherapy exist several invasive and non-invasive procedures:
First, man stiffens the growth plate in the short term the side of the knee that is growing too quickly. The growth plate is the part of the bone where the Bone growth takes place. While this is already closed in adults, in children it is in one constant construction and dismantling process.
A short-term stiffening The result is that at this point the bone remains for a certain period of time does not continue to grow. Meanwhile, the outside of the knee has time to grow back - because it is logically not stiffened.
In the best case, the result is one horizontal straightening of the knee joint. The disadvantage of this method is that it Growth in length impaired becomes. On the other hand this is The intervention is not particularly large, and can be done quickly. A stiffening of the growth plate can also permanently respectively.
A another operative method is the Removal of a piece of bone (mostly from the iliac crest) and subsequent implantation on the "too short" side (in the case of the knock knees, the outside). This compensates for the "inward kink". However, it is not absolutely necessary to remove a piece of bone, it can also be lengthened by means of metal plates or screws be made.
The great advantage of this surgery is that patients mostly do one day after the operation already again ambulatory are (on crutches) and can do physiotherapy. In this way, the muscular system can also adapt to the unusual loads at an early stage.
A Full load of the knee is again after such a "conversion operation" after 2 months possible, the plates and screws are usually removed 1.5 years after the operation, when the bone has grown back sufficiently. This type of surgery can be a great pain relief achieve, and also in the long term (10 years and more) normal sporting activity enable.
In addition to the operative procedure there is the so-called Leg axis trainingwhich aims to achieve the knock-kneed position Strengthening the surrounding muscles to correct. Exercises like Squats to strengthen the Thigh muscles, or self-control through exercises in front of the mirror under professional guidance also achieve a correction of the deformity.
This is especially useful in adult patients where the process is more advanced.
How are knock knees treated?

Kick the Knee legs in the growth phase, therapy is usually not necessary. However, the affected children should be observed and their legs checked. After long observation shortly before the end of growth there is no spontaneous improvement in the Knee legs occurred or the axis deviation is more than 20 degrees, surgical therapy may be necessary. Several methods can be used here:
- (wedge) Osteotomy (here a mostly wedge-shaped piece bone removed to compensate for the misalignment)
- temporary Epiphysesodesis (here the growth plate (Epiphysis) temporarily stiffened so that the leg cannot grow any further)
- definitive Epiphysesodesis (In contrast to temporary epihyseodesis, the growth plate is permanently stiffened here)
Even with one rickets (Vitamin D- Deficiency) deformation of the legs caused by deformation can recede spontaneously - provided the deformities are not too pronounced. Because if the legs are bent too much, the muscle pull can further increase the deformation.
In children and adults, insoles in the shoes can compensate for the misalignment somewhat. In the case of the knock knees, the insides of the soles are reinforced so that the Buckle foot can be balanced. The burden in Knee joint is shifted laterally (outside).
Inlays with raised inner edge
As it is with Knock knees If it is a congenital misalignment of the feet, other joints may also be impaired over time.
Above all, the knee joints, hips and spine can be long-term affected by pronounced knock knees.
There are basically various methods that can be used to treat the knock knees. Due to the misalignment of the feet, there is increased stress in the area of the inner edge of the feet, at the same time the stress on the outer edges of the foot is significantly reduced.
Special insoles with Inner rim elevation can lift the foot and thus compensate for the misalignment. However, these insoles cannot always prevent the impairment of other joints despite a special increase in the inner edge.
The chances of success of this form of treatment depend on various factors.
Above all, the shape of the knock knees and the age at which the orthotics start to be worn play a decisive role in this context. In general, it can be assumed that starting treatment as early as possible and consistently wearing the insoles with a raised inner edge can significantly increase the chances of success.
Especially in older patients, the options for insole therapy are quite limited. If wearing the insoles does not compensate for the knock-knees despite the increase in the inner edge, an alternative treatment should be considered.
Depending on the severity of the foot deformity, surgical removal of a portion of the bone or stiffening of the growth plate may be considered.
Exercises (abductors, lat. Vastus muscle - towards bow leg)
Especially with children who suffer from pronounced knock knees, special exercises can help to compensate for the causal foot deformity.
Above all a structure of the so-called Abductors should help to stabilize the leg axis and thus counteract the long-term effects of the knock knees.
The abductor group includes the muscles on the outside of the legs. The abductors of the foot itself can be stabilized through specific exercises and help to strengthen the ankle in general.
In this way, the congenital foot deformity is to be compensated slightly. In addition, affected patients should be given special exercises at regular intervals to strengthen the Vastus lateralis muscle carry out.
This muscle is also called the external broad thigh muscle designated. From an anatomical point of view, the vastus lat. Muscle is not an independent muscle, but only one of the four heads of the large thigh muscle (Quadriceps femoris muscle). People who suffer from pronounced knock knees can correct the misalignment of the leg axis through specific exercises of this muscle.
When performing the special exercises for correcting knock knees, however, it must be noted that the abductors and vastus lat. Muscles must never be trained in isolation. In addition to these muscles, other muscle groups, such as the Adductors of the Inner thigh, being constructed.
Otherwise there is a risk that the misalignment of the leg axis will be shifted towards the bow legs. A shift in the leg axis in the direction of bowlegs can, in the long run, impair various joints, for example the ankles, the knee joints, the hips and the spine.
prophylaxis
An early operation to straighten the axial misalignment can prevent osteoarthritis of the knee. The misalignment of the axis can be prevented depending on the cause.
Corrections during growth can only be carried out by epiphysodesis. This means the desertification of a growth plate. However, the prerequisite is that there is still growth. By deliberately obliterating a growth plate on one side, the bow leg grows straight until the end of growth.
The so-called bone age must be determined in order to achieve the right time for the obliteration and correct outgrowth.
From the bone age the Determine your height and determine the exact time of the epiphyseodes.
You can find more information on determining your height at: Orthopedicum - body size determination.
Problems with knock knees
In the long term, all high-grade leg malpositions, whether knock knees or also If a to premature wear of the Articular cartilage, so that with increasing age with a arthrosis of the knee joint (Knee osteoarthritis, Gonarthrosis) must be expected. In the case of the knock knees, the outer knee joint is particularly affected, while with bow legs an internal knee osteoarthritis comes into play.
However, the extent of osteoarthritis depends on other risk factors such as Obesity, Connective tissue weakness, accident and injuries etc.
Knock knees in children
Although knock-knees in adulthood are assumed to be congenital deformities of the feet, knock-knees that occur up to school age do not have to be pathological.
If knock knees occur in children, it can primarily be assumed that this misalignment is due to delayed growth. As the body grows, it can be observed in most cases in affected children that the knock knees completely recede without medical intervention.
Knock-knees or bow-legs can be seen in around 20 percent of children before the age of six. However, in routine examinations from the age of 10, these knock knees have completely regressed in around 80 percent of cases.
Parents who are unsure about their child's leg axis misalignment should consult a specialist. The normalization of this deformity can often be supported by targeted training of the muscles.

















.jpg)